ROE Calculator
Return on Equity (ROE) Ratio Calculator and Formula.
Insert Net Income and the Total Equity into this Return on Equity ROE Calculator.
Information can be found through a Google search, in the annual report on the company’s website under “Investor Relations,” or on financial websites.
Our Premium Tool applies a variety of different valuation models and automatically loads the necessary data. Find stock valuations and financial ratios to more than 45.000 stocks worldwide.
What is the Return on Equity ROE Calculator?
Return on Equity or ROE is a relative valuation ratio which uses the net profit generated by the company and its shareholder equity to determine how efficiently the company is generating its profits when compared to its peers as well as to the average of the industry in which it operates. Unlike other relative valuation metrics, ROE is unique in that it can be used to compare companies across industries and sectors alongside companies in its own unique sector.
In essence, Return on Equity tells you how much bang for your buck you are likely to receive from the company where your buck is. This is an important metric to know irrespective of the sector because even though the company might be the best in the sector if the ROE is low as compared to other sectors, you are better off investing in the high ROE sectors and ignoring the low ROE ones. Knowledge is easily processed when accompanied by an example so let us look at one while we try to understand this ratio in detail.
Formula ROE:
ROE (%) = (Net Profit or Income / Shareholder Equity) * 100
Both values are available in the financial statements of companies with Net Profit available in the Income statement and Shareholder Equity in the Balance sheet. Shareholder Equity can also be calculated by subtracting all liabilities from all assets.
At its core, Return on Equity measures how much return the company is generating for its shareholders and how efficiently it is growing its capital. An ROE of 30% means that the company is earning 30% on its invested capital every year and a growing ROE means that return is growing as well. That does not mean that all you have to do to invest successfully is identify high ROE companies and invest in them.
This ratio is not the Holy Grail of company evaluation. As with other valuation metrics, there are some drawbacks to its application which we shall see below but it is a handy tool to highlight strong companies in their sectors.
Example:
As mentioned at the start, Return on Equity can be sector agnostic. To showcase this special feature of sectorial independence, we shall look at the most popular companies in the world right now: Apple Inc., Amazon Inc., Alphabet Inc. (Google), and Netflix Inc. We shall look at the ROE of these companies and compare them with their performance over the last year. As with other ratios, ROE is independent of currency as long as both Net Profit and Shareholder Equity are considered in the same currency.

If I was an investor looking to make the maximum return, I would want to invest in a high ROE company like Apple. Although share performance is not dependent on Return on Equity alone, a company’s ability to generate high ROE is a significant factor in appreciating share prices. This also highlights one of the drawbacks of ROE. Just by looking at these numbers, it is difficult to make out which is a market leader in their respective sector and which isn’t. Let us look at performances to highlight that better.
Netflix which was a market leader once upon a time has to now compete for its position with several new and powerful entrants like Hulu, and Disney+. Apple TV, Peacock, Amazon Prime and many more. Its returns have now lined with its Return on Equity. Apple too has to compete for its phones with several large players like Samsung, Xiaomi, and local manufacturers but it continues to remain a large force in its sector aligning its returns with its ROE as well.
Amazon is a market leader in online retailing and continues to dominate the sector. It gained an especially high market share during the pandemic when physical retail outlets were shut but online deliveries remain. It has also diversified into other segments like web hosting services where it is again a leader, streaming services, and many more.
Finally, Google which is not only the dominant player in search engines and mobile operating systems with Android but also a paramount example of a pandemic-proof business and its investors have been rewarded for that pandemic resilience with a phenomenal appreciation in share price.
What you should be looking for:
ROE might come across as a one-stop solution for company valuation and like a siren song that attracts sailors to go overboard on their ships, ROE numbers might entice investors to go overboard with their company selection choices. A single ROE number in its absolute is a disaster waiting to happen.
It is influenced by Net Profit and Shareholder Equity. Let us look at Net Profit first. In any one year, the company may have sold a large piece of asset or had a one-time windfall which will be recorded in its Net Profit thus increasing its ROE by default and giving an incorrect impression that the company has grown earnings well. In the case of Shareholder equity, a buyback will automatically reduce shareholder equity and increase ROE without any meaningful change in the company’s ability to generate that ROE.
By default, it is recommended to calculate the average ROE of 5 years by calculating the ROE of each year and then taking their average. A high ROE is no indicator of the debt problem in the company. ROE effectively serves as a speed breaker bump. A company can grow its earnings only as fast as the ROE. For it to increase its ROE, it will have to bring in more cash either via the issue of shares which will increase shareholder equity and suppress ROE in the short term but improve over the long term, or take on debt to get that additional cash.
A company can simply choose to take on more and more debt which will increase liabilities and reduce shareholder equity (Assets minus Liabilities) thus increasing ROE. So what is high ROE might simply be a debt-laden company.
Ideally, a high ROE is a good indicator of the market leadership of the company in its respective sector. However the same should be established by taking a deep dive into company financials to see if that ROE has come on the back of increasing debt or by virtue of business operations. A high ROE must be backed by sound business practices for it to be a sound investment. Let us look at some companies in the same sector to highlight the drawbacks as well as what we should be looking for.
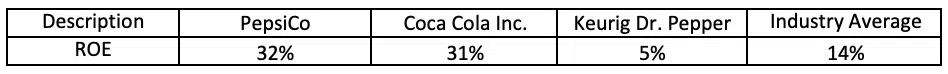
As you can see, Keurig Dr. Pepper has a low ROE as compared to its giant peers Pepsi and Coca-Cola. It has a lower ROE than the industry average as well but you will be surprised to see their performance in the last year.
Surprising isn’t it? The reason behind this requires us to take a peek at their financials!
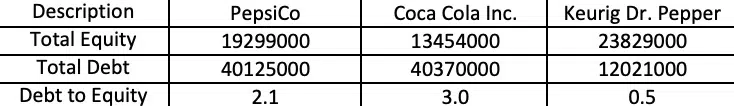
Pepsi and Coca Cola are highly leveraged as compared to Dr. Pepper and their ROE has been inflated because of that as well. However market is supreme and it has realized that the ROE number is for show and that actual returns will not be as high and the same is reflected in the appreciation of their share price. You can try this exercise out on any sector here at fairvalue-calculator.com itself.
In my experience, ROE is a good filter to knock out those that destroy shareholder value. Average market returns can be found by a simple Google search. Ideally you want a company, especially one you wish to invest in to generate a ROE higher than average market return which we can consider on the higher side at 16%. Any company generating ROE lower than this is just burning cash and in the long run will fail because it will be unable to raise any money from the markets and its profits are not enough to grow capital.
An investor too would be better off putting his/her money in an index fund rather than a low ROE company. Once the filter has been applied, other valuation metrics can be used to sift through the high ROE companies and a consensus of valuation metrics can then be used to create a final short list which an investor can then explore in depth before making their investment decision.
In our Premium Tools we already analyzed more than 45.000 stocks worldwide to find fair values and to interpret the ROE.
